Transforming Water Distribution Management with IoT Technology
Jal Jeevan Mission: A Commitment to Every Household:
The Jal Jeevan Mission aims to provide assured potable water through taps to all rural households by 2024. A key objective of the mission is to ensure a consistent supply of water at 55 liters per capita per day (LPCD), adhering to the quality standards prescribed by BIS 10500:2012. The mission emphasizes delivering Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) to every household in rural Maharashtra, setting benchmarks for service delivery and ensuring water as a sustainable service for all.
Leveraging IoT for Smart Water Management:
Recent advancements in electronics, communication, and data analytics have paved the way for smarter and more efficient water management systems. CS TECH Ai’ IoT-enabled solution integrates innovative technologies to monitor and manage water distribution at multiple levels effectively.- IoT-Enabled Devices: The solution uses sensors such as flowmeters, pressure sensors, and residual chlorine detectors to collect real-time data on water quantity, quality, and distribution network health.
- Data Transmission and Centralized Monitoring: Data from village-level devices is transmitted to a centralized cloud server at the state level and simultaneously shared with local operators at the Gram Panchayat level to ensure reliable and actionable insights.
- Fraud Detection and Data Integrity: Features like fraud detection mechanisms ensure the authenticity and integrity of the data collected.
- Real-Time Dashboard: A centralized real-time dashboard continuously monitors key performance indicators, including water supply levels, chlorine concentration, and groundwater levels. This enables authorities to mitigate risks such as contamination, source depletion, or system failures promptly.
Work We Did: A Comprehensive Approach:
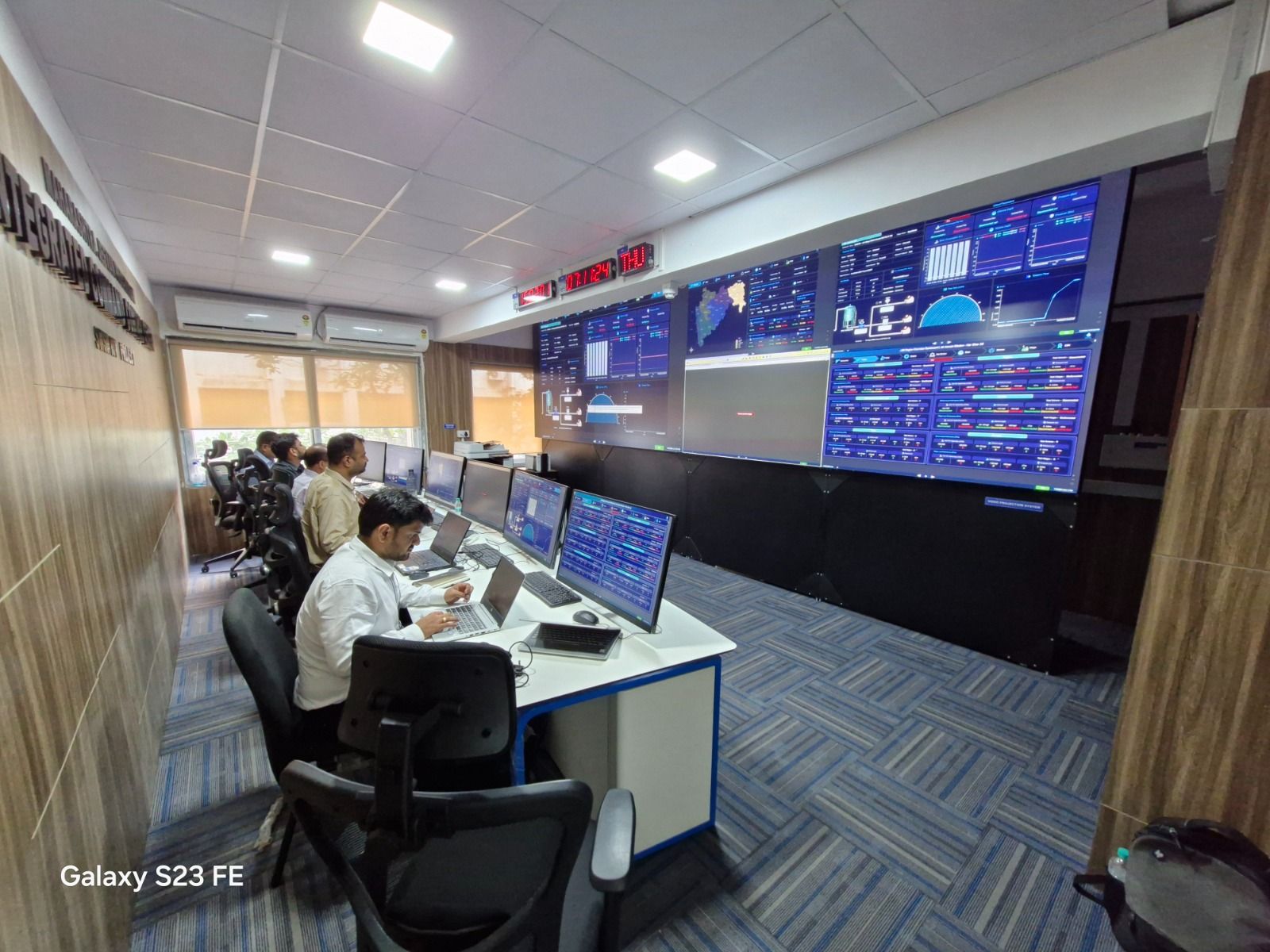
CS Tech Ai has undertaken a multifaceted approach to implement IoT solutions across 10 districts in Maharashtra, including establishing an Integrated Command and Control Center (ICCC) in Mumbai.
- Surveys and Data Collection:
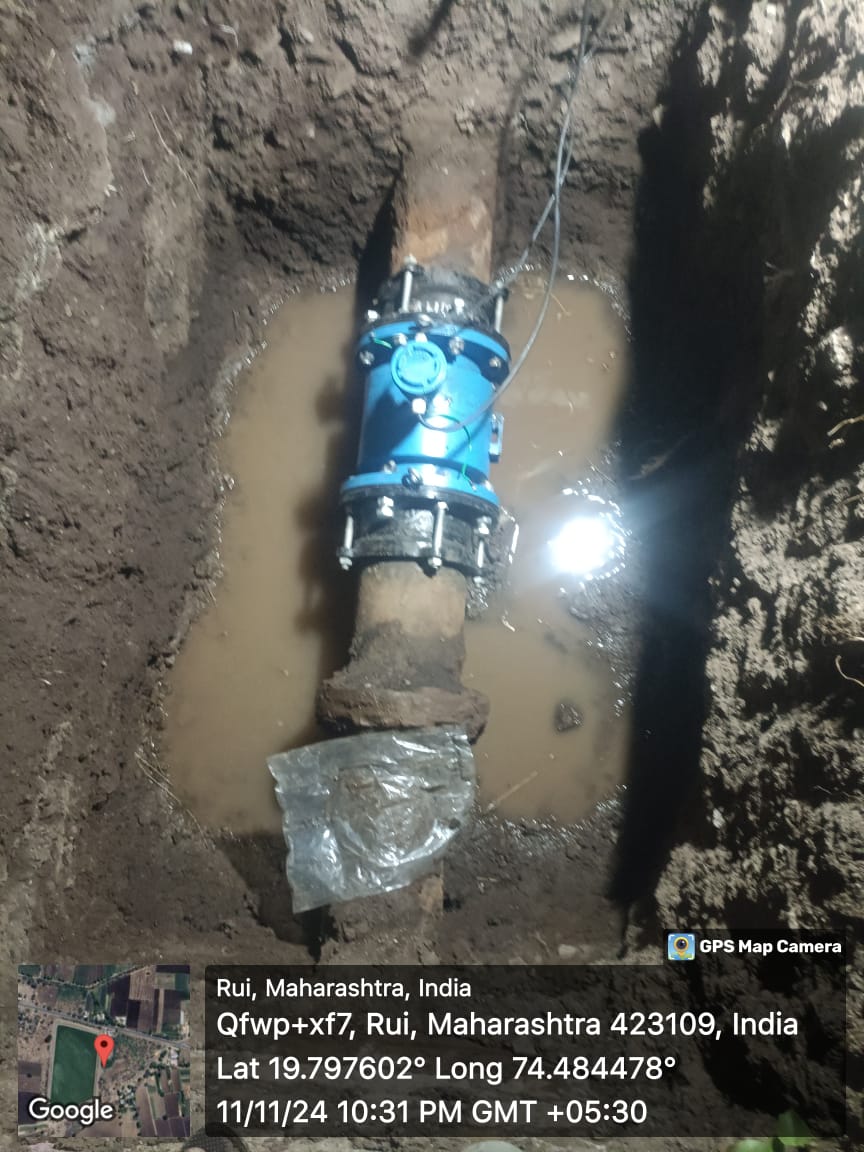
Surveys were conducted for 181 water supply schemes across the districts, collecting critical data to tailor the solution to local needs. - Design and Implementation:
The design phase ensured solutions were aligned with the unique requirements of each district. The first batch of IoT sensors was deployed, and installation activities began, focusing on key parameters like water quality, flow rates, and distribution network health. - Integrated Command and Control Center (ICCC):
The ICCC serves as the central hub for monitoring and managing rural water systems. Its dashboard provides near real-time insights into water supply performance, enabling timely interventions and improved operational efficiency. - Integration Activities:
The system integrates data from various sources, ensuring seamless communication between IoT sensors, the ICCC dashboard, and command centers, thereby enhancing the reliability of water supply systems.
Key Outcomes Achieved:
The IoT solution delivers measurable benefits across multiple levels:
- District Level:
- Track functional vs. non-functional schemes and days of non-functionality.
- Monitor schemes meeting the ≥55 LPCD standard and average daily water supply duration.
- Identify and address outages or contamination incidents promptly.
- Block, Village, and Habitation Levels:
- Analyze demand vs. supply metrics and non-revenue water.
- Monitor water outages or contamination incidents.
- State Level:
- Assess service delivery indicators such as LPCD supplied, water supply duration, water quality, and groundwater levels.
- Ensure schemes meet the ≥55 LPCD standard and address any non-conformance to water quality benchmarks.
Benefits to Society and Governance:
The IoT solution provides far-reaching socio-economic and operational benefits:
- Improved Service Levels:
Enhanced transparency and accountability ensure consistent and equitable water supply, improving quality of life and public health. - Data-Driven Decision-Making:
Advanced analytics support evidence-based planning for new schemes, modifications, and preventive maintenance. - Operational Efficiency:
Reduced costs and extended lifecycle of water supply schemes through efficient resource utilization, leak detection, and proactive maintenance. - Sustainability:
Improved monitoring of water sources ensures long-term sustainability and responsible water use by consumers. - Centralized Oversight with Local Action:
Integration from village to state level enables a coordinated response to any issues, fostering trust and reliability in public service delivery.
Conclusion: A Blueprint for the Future:
CS Tech Ai’s IoT-based solution under the Jal Jeevan Mission exemplifies how technology can transform water management, ensuring every household in Maharashtra has access to safe and sufficient water. By integrating IoT devices, centralized monitoring, and real-time analytics, the project sets a benchmark for future initiatives in water infrastructure and governance. It is a testament to how technology and innovation can drive impactful change for communities and ecosystems alike.